- Gold price attracts safe-haven flows for the third straight day amid rising trade tensions.
- Fed rate cut bets weigh on the USD and also lend support to the non-yielding yellow metal.
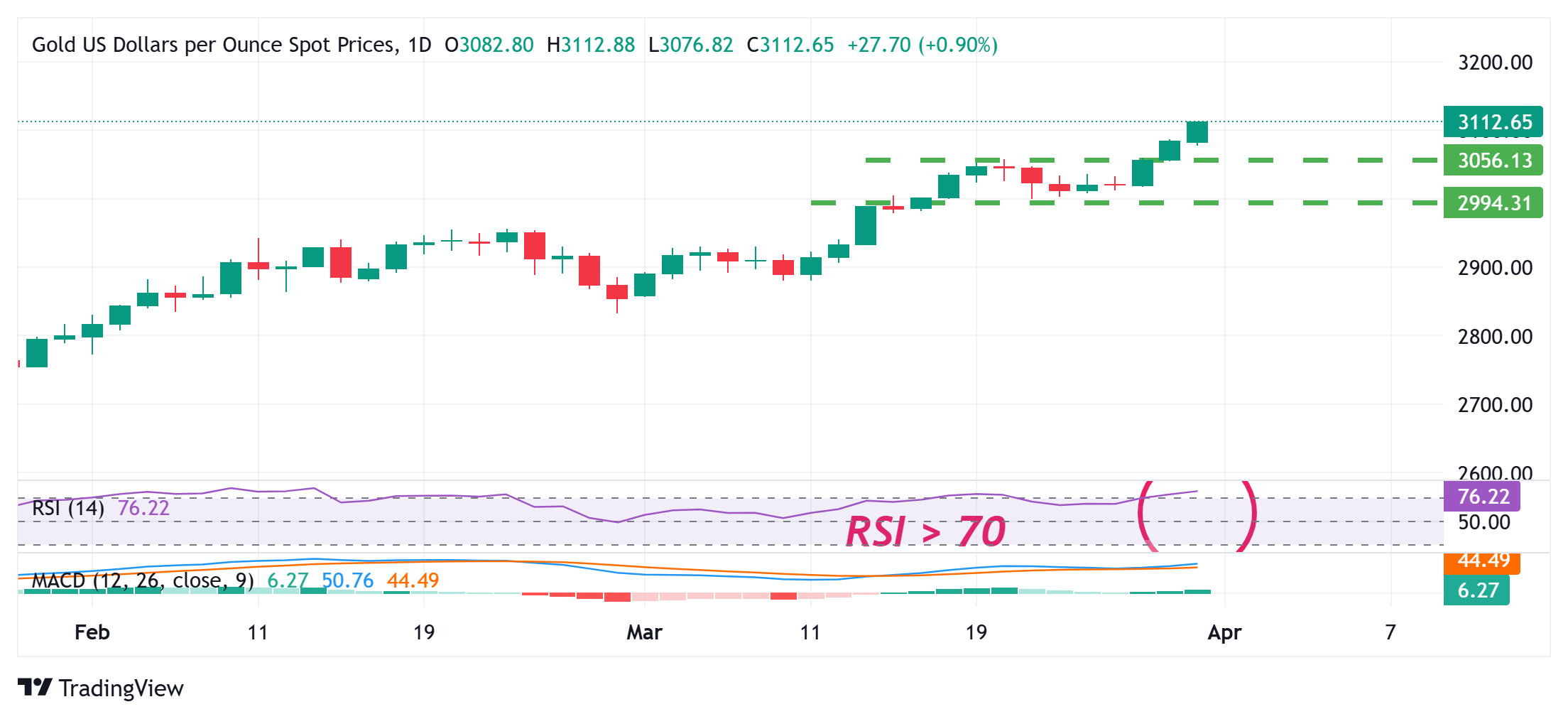
- Overbought conditions on the daily chart now warrant some caution for bullish traders.
Gold price (XAU/USD) retains its bullish bias through the first half of the European session on Monday and is currently placed near the all-time peak, just above the $3,120 area. The uncertainty over US President Donald Trump’s so-called reciprocal tariffs, along with heightened fears of a US recession and geopolitical risks, continues to weigh on investors’ sentiment. The anti-risk flow is evident from a generally weaker tone around the equity markets and pushes the safe-haven precious metal higher for the third successive day.
Meanwhile, the growing acceptance that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will resume its rate-cutting cycle soon amid concerns about a tariff-driven US economic slowdown keeps the US Dollar (USD) bulls on the defensive. This turns out to be another factor driving flows toward the non-yielding Gold price and supports prospects for an extension of a multi-month-old ascending trend. However, bulls might pause for a breather amid overbought conditions on the daily chart and ahead of this week’s key US macro releases.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Gold price buying remains unabated as US tariff uncertainty continues to boost safe-haven demand
- US President Donald Trump rattled markets last week by imposing a 25% levies on all non-American cars and light trucks ahead of the so-called reciprocal tariffs set to take effect on April 2. Adding to this, the Wall Street Journal reported on Sunday that the Trump administration is considering higher trade tariffs against a broader range of countries, pushing the safe-haven Gold price to a fresh record high during the Asian session on Monday.
- Trump said on Sunday that he was very angry and pissed off at Russian President Vladimir Putin, and threatened massive tariffs on Russian oil and potential bombings in Iran. Trump also lashed out at Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy and warned that he would face big problems if he backed out of the critical rare earth minerals deal. This further weighs on investors’ sentiment and contributes to the global flight to safety.
- Meanwhile, US data released on Friday showed that the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index rose 0.3% in February and 2.5% from a year ago – in line with market expectations. However, the core gauge, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, showed a 0.4% increase for the month. This marked the biggest monthly gain since January 2024 and lifted the 12-month inflation rate to 2.8% during the reported month.
- Additional details revealed that Consumer Spending accelerated 0.4% following a downwardly revised 0.3% fall in January, while Personal Income posted a 0.8% rise during the reported month. Separately, a survey from the University of Michigan showed that consumers’ 12-month inflation expectations soared to the highest level in nearly 2-1/2 years in March, which further benefits the precious metal’s hedge against rising prices.
- This comes on top of persistent worries about slowing US economic growth and fuels stagflation fears, dragging the US Dollar lower for the third straight day and further offering support to the XAU/USD pair. The commodity reacts little to China’s official Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), which showed that the Manufacturing PMI edged higher to 50.5 while the Non-Manufacturing PMI jumped to 50.8 in March.
- Traders now look forward to this week’s important US macro releases scheduled at the beginning of a new month, including the closely-watched Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report on Friday. In the meantime, overbought conditions might hold back bulls from placing fresh bets and cap the yellow metal. The fundamental backdrop, however, suggests that the path of least resistance for the commodity remains to the upside.
Gold price technical setup supports prospects for additonal gains; overbought RSI on the daily warrants some caution
From a technical perspective, Friday’s sustained breakout above the previous all-time peak, around the $3,057-3,058 region, was seen as a fresh trigger for bullish traders. That said, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) on the daily chart remains above the 70 mark for the third straight day and points to overstretched conditions. Hence, it will be prudent to wait for some near-term consolidation or a modest pullback before positioning for an extension of the recent well-established uptrend witnessed over the past three months or so.
Meanwhile, any corrective pullback below the Asian session low, around the $3,076 area, now seems to find decent support near the aforementioned resistance breakpoint. This is followed by the $3,036-3,035 support zone, below which the Gold price could accelerate the slide back towards retesting the $3,000 psychological mark. The latter should act as a key pivotal point, which if broken decisively might shift the near-term bias in favor of bearish traders and pave the way for deeper losses.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.